Square gyrobicupola
| Square gyrobicupola | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | Bicupola, Johnson J28 – J29 – J30 |
| Faces | 8 triangles 2+8 squares |
| Edges | 32 |
| Vertices | 16 |
| Vertex configuration | 8(3.4.3.4) 8(3.43) |
| Symmetry group | D4d |
| Dual polyhedron | Elongated square trapezohedron |
| Properties | convex |
| Net | |
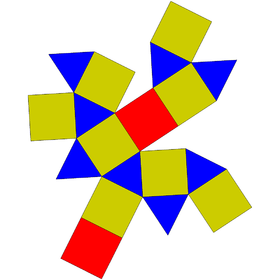 | |
In geometry, the square gyrobicupola is one of the Johnson solids (J29). Like the square orthobicupola (J28), it can be obtained by joining two square cupolae (J4) along their bases. The difference is that in this solid, the two halves are rotated 45 degrees with respect to one another.
A Johnson solid is one of 92 strictly convex polyhedra that is composed of regular polygon faces but are not uniform polyhedra (that is, they are not Platonic solids, Archimedean solids, prisms, or antiprisms). They were named by Norman Johnson, who first listed these polyhedra in 1966.[1]
The square gyrobicupola is the second in an infinite set of gyrobicupolae.
Related to the square gyrobicupola is the elongated square gyrobicupola. This polyhedron is created when an octagonal prism is inserted between the two halves of the square gyrobicupola.
Formulae
[edit]The following formulae for volume and surface area can be used if all faces are regular, with edge length a:[2]
Related polyhedra and honeycombs
[edit]The square gyrobicupola forms space-filling honeycombs with tetrahedra, cubes and cuboctahedra; and with tetrahedra, square pyramids, and elongated square bipyramids. (The latter unit can be decomposed into elongated square pyramids, cubes, and/or square pyramids).[3]
References
[edit]- ^ Johnson, Norman W. (1966), "Convex polyhedra with regular faces", Canadian Journal of Mathematics, 18: 169–200, doi:10.4153/cjm-1966-021-8, MR 0185507, Zbl 0132.14603.
- ^ Stephen Wolfram, "Triangular gyrobicupola" from Wolfram Alpha. Retrieved July 23, 2010.
- ^ "J29 honeycomb".


